What is a Multi-Step Income Statement?
The multi-step income statement is an in-depth analysis of the business’s financial performance during a specific reporting period.
[ez-toc]
The financial statement categorizes the business’s revenues and expenses into operating and non-operating activities.
Operating activities cover revenues and expenses directly related to a business’s primary activities. In contrast, non-operating activities include items, revenues, and expenses unrelated to the core business operations.
Some components of multi-step income statements include;
- Revenues (Net Sales)
- Cost of Goods Sold
- Gross profit
- Operating expenses
- Non-operating expenses
- Interest income (expense)
- Net income before taxes
- Income tax expense
- And Net Income (loss)
The siloed breakdowns in multiple-step income statements give stakeholders a razor-sharp view of how a company runs its business operations by detailing how the gross, operating, and net margins compare.
Public companies and large manufacturing businesses with multiple revenue sources often use multi-step income statements.
How to Create A Multi-Step Income Statement? Understand with Examples
Accountants prepare multi-step income statements as per generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP).
Process of creating a multi-step income statement
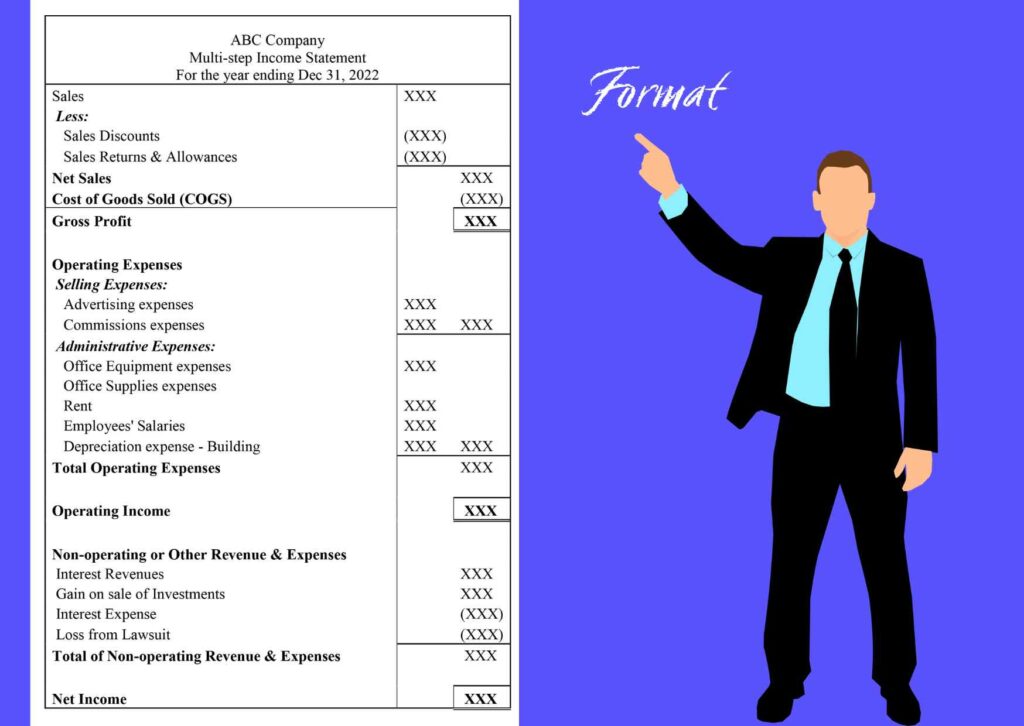
Preparing a multiple-step income statement involves the following steps;
- Define period – The first step towards preparing a multi-step income statement is to decide whether you will track monthly, quarterly, or annual expenses.As per the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC)’s Required Disclosure Documents, publicly traded companies must prepare quarterly and annual financial statements.
Creating monthly multi-step statements can help track a company’s profits over time, which can be useful for making financial decisions about the business. For example, whether to invest money in new equipment or divert it towards other operating expenses. - Create document header: The header of the multi-step income statement conveys important information. It states a company’s name, identifies the document as an income statement, and defines the period covered by the document.
- Add all operating expenses: This includes the cost of goods sold and other indirect costs such as employees’ salaries, advertising expenses, insurance, depreciation and amortization, and administrative expenses, including office supplies, electricity, and rent.
- Include all non-operating revenues and expenses: In the bottom section of the income statement, below operating activities, create a section for non-operating activities and input all revenues and expenses from non-operating activities. Non-operating activities generally include insurance proceeds, interest revenue, loss from lawsuit settlements, and the sale or purchase of investments.
- Apply Formulas – There are three formulas for preparing the multi-step income statement; Gross Profit, Operating Income, and Net Income.
- Gross profit formula – To calculate the gross profit of your multi-step income statement, use the formula:
Gross Profit = Revenue (or Net Sales) – Cost of Goods Sold
In multi-step income statement, gross profit is shown as the difference between net sales and cost of goods sold. - Operating income formula – To determine the operating income, apply the formula:
Operating Income = Gross Profit – Operating Expenses
Identify and add all the operating and administrative expenses and then subtract the total from gross profit. The resultant is shown as income from operations or net operating income. - Net income formula – To compute net income apply the formula:
Net income Formula= Operating Income + Non-Operating Items
Put the total at the bottom of the income statement as Net Income. If it is a positive number, then the business is reporting a profit. In contrast, a negative number indicates recording a loss by the business.
- Gross profit formula – To calculate the gross profit of your multi-step income statement, use the formula:
Once you have completed all the steps to prepare a multi-step income statement, your income statement will appear as the sample given below.
Numerical examples of the multi-step income statement
Let’s explore a few examples of the multi-step income statement.
Example 1: Company A has a sales turnover of $200,000. Find out the gross profit if the Cost of gold sold of value is $50,000, insurance proceeds stand at $19,000, and rent is $33,000.
Solution: Find out the gross profit, we will apply the formula:
Gross Profit = Revenue (Net Sales) – Cost of Goods Sold
We get => 200,000 – 50,000 = $150,000
We shall not include insurance proceeds as it is a non-operating expense, and rent will fall under operating overhead.
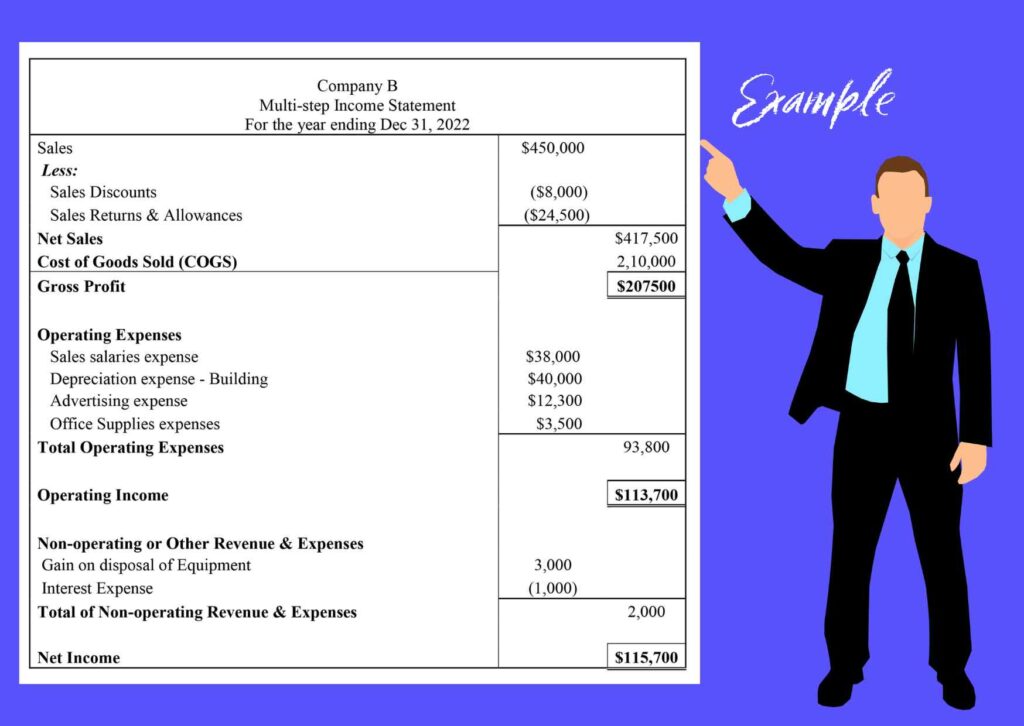
Example 2: A portion of the adjusted trial balance for Company B is shown below. Create a multi-step income statement based on the data given below.
- Sales are $450,000 (net sales discounts of $8,000 and sales returns and allowances of $14,500)
- Cost of goods sold = $210,000
- Salaries expense = $38,000
- Depreciation of building = $40,000
- Advertising expense = 12,300
- Office supplies expense = $3,500
- Gain on disposal of store equipment = $3,000
- Interest expense = $1,000
Solution: We will follow a three-step process to find the solution.
First, prepare the Gross Profit section. We will include the following items from the data; Sales = $450,000, Sales Discounts = $8,000, Sales returns and allowances = $24,500, and Cost of goods sold 210,000.
We will subtract Sales Discounts and Sales returns and allowances from Total sales of $450,000 to get Net Sales = $417,500
Then apply the formula:
Gross Profit = Revenue (or Net Sales) – Cost of Goods Sold
=> 417,500 – 210,000= 207,500
Second, identify and add all the operating expenses. These include all indirectly related costs like Salaries expenses, Depreciation of building, Advertising expenses, and Office supplies expense.
We get => 38,000 + 40,000 + 12,300 + 3,500 = 93,800
Then calculate the Operating Income by applying the formula:
Operating income = Gross Profit – Operating Expenses
=> 207,500 – 93,800 = 113,700
Third, identify and compute all the items for the Non-Operating head. These include Gain on disposal of store equipment and Interest expense. The expense will be reduced.
We get => 3,000 – 1,000 = 2,000
Then calculate net Income by applying the formula:
Net income Formula= Operating Income + Non-Operating Items
=> 113,700 + 2,000 = $115,700
Pros
There are many advantages of using a multi-step income statement for the business. Some of these include;
- Offering in-depth details to stakeholders about the primary and non-primary business activities.
- The multi-step income statement gives a comprehensive view of a company’s operating income from various sources of revenue and the costs associated with producing that revenue. It calculates the net income for a particular period.
- Potential investors and creditors can ask for/ or use a multi-step income statement to analyze the gross margin (gross profit divided by revenue) and check the efficiency of the company’s operations for decision-making. Analysts can use the gross profit margin calculation to compare multiple companies’ products to identify the best performer.
- Extraordinary items are shown under the ‘non-operating items’ head to indicate that they are ‘one-off events’ and will not recur every period. A stock analyst can ignore these while valuing a business entity for a potential merger and acquisition scenario.
Cons
Here are some drawbacks of using the multi-step income statement.
- Lengthy Preparation Time – Preparing a multi-step income statement is a time-consuming process. There are separate categories for business incomes, and each provides a detailed list of revenue and other expenses incurred under them. So, more time is spent analyzing financial data and putting it into the statement.
- Confusing – Due to the in-depth details and length of the multi-step income statement, some users may need help interpreting how items and calculations are shown. For example, users may have difficulty comprehending the meaning of individual line items within the operating and non-operating income heads.People may prefer a single-step income statement as it offers the use of a single equation to calculate the net income. In contrast, a multi-step income statement is a three-step process that includes equations for gross profit, operating income, operating expenses, and net income.
- Higher due diligence necessary – A single mistake in the multi-step income statement can cause investors to make errant assumptions about the core business activities, which can negatively impact the company.
When to Use it?
Larger and publicly-traded companies typically use multi-step income statements.
Large corporations tend to prepare multi-step income statement due to the size and complexity of their businesses. Businesses of large manufacturing companies and giant retailers usually have various revenue streams, and they will need to record the income in different accounts.
Publicly-traded companies are required by law to quarterly and annually file the multi-step income statement, one for the agency itself and the other for the company’s stakeholders and other users.
Small businesses looking to raise funds from investors and creditors can also use multi-step income statements. The multi-step income statement gives them greater detail about the business’s total revenue and expenses, which can help them assess its long-term viability.
With the single-step layout, details like total operating expenses, non-operating revenue, and other expenditures are left out of the presentation and calculation of net income. The layout of the multi-step will allow the user to see the performance of the components of the operating and non-operating head.
Are you looking for accounting software to help you generate your income statement at the click of a button? Look no further!
Akounto is here to take up all your worries for record-keeping, preparation, and management of financial statements. Sign-up with Akounto today to outsource your sensitive accounting tasks to professionals and experts.